Selecting the right AI tools can be a daunting task for many business owners, simply because there are so many options.
With more than 2,000 AI tools available worldwide, and over 1,500 designed specifically for business use, it’s impossible to test them all to find the perfect fit.
As a result, many business owners end up relying solely on ChatGPT, often using it as nothing more than a more descriptive version of Google search.
We can help you cut through the noise and identify the AI tools that deliver measurable business results.
In this article, we will:
- Break down AI tools by their popularity and use case category.
- Show you how to connect your data with AI tools to maximize business value.
- Demonstrate measurable results from testing four top AI tools on a route-optimization task.
How to Make Sence of 1,500 AI Tools for Business
AI Tools Ranked by Popularity and Category
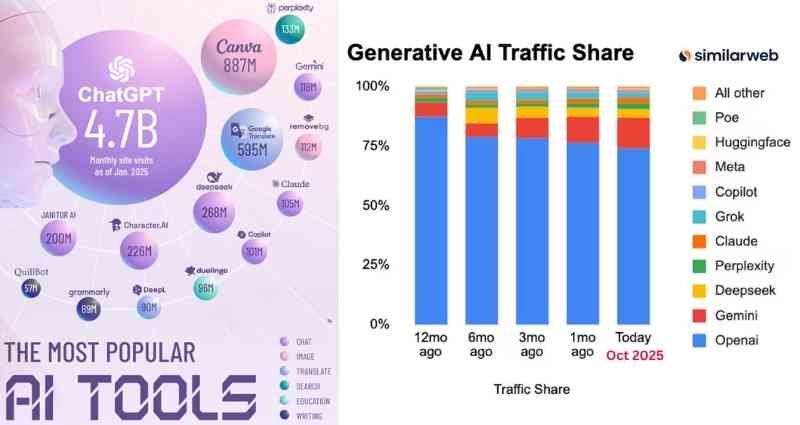
The chart on the left, titled “The Most Popular AI Tools” by Visual Capitalist, illustrates the evolving landscape of AI adoption as of January 2025, measured by monthly site visits. ChatGPT leads by a wide margin with 4.7 billion visits, reinforcing its dominance as the most widely used AI tool globally. Canva, which integrates AI for design and image generation, ranks second with 887 million visits, followed by Google Translate at 595 million.
Other notable tools include Character.AI (226M), Gemini (118M), Claude (104M), Perplexity (133M), and Copilot (96M). The leading use-case categories represented are chat, image generation, translation, search, education, and writing, highlighting AI’s rapid integration into both creative and productivity workflows.
The chart on the right, “Generative AI Traffic Share” from Similarweb, provides a broader view of market dynamics over the past year. While ChatGPT’s dominance remains clear, its share has slightly decreased as competitors such as Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, and Copilot gain traction. This gradual shift suggests a maturing generative AI market where users are increasingly exploring specialized tools tailored to different tasks and ecosystems rather than relying solely on a single platform.
What does it mean for business owners?
The diminishing dominance of ChatGPT and the rise of other AI tools signal that generative AI has moved beyond experimentation into mainstream business use. For business leaders, this means AI is no longer a niche productivity booster. It’s becoming a foundational capability that shapes how organizations create, communicate, and compete.
According to the study “How People Use ChatGPT,” roughly 40% of all business-related interactions on the platform involve writing tasks, from crafting marketing copy and customer emails to producing reports and internal communications.
This concentration shows that writing is currently one of the most mature and widely adopted AI use case. In most cases adopting AI for content creation and internal workflows offers an immediate, low-risk entry point with tangible ROI.
Winning with Your Data and Processes
Most AI tools are trained on vast public data, billions of documents that give them broad general knowledge but no insight into your specific business question. Training data, which provides general intelligence lacks your specific business context.
You can customize your AI tool to move it one level up toward understanding your business setting. Customization helps AI communicate and work the way you need it to. This includes defining tone, level of detail, format, and even how cautiously it should make assumptions.
But the real game-changer is project knowledge: the data you upload or connect, such as your product descriptions, pricing, customer feedback, competitive information, procedures and instructions. When an AI can use your own materials, it starts generating insights, plans, and content that align with your operations and goals.
Let’s take an example of a business plan, one created using only public data, and another powered by your own business data.
When you ask an AI tool to “write a business plan” without providing any context, it pulls from general market information and common templates found in its training data. The result might look professional, but it’s broad, full of assumptions, and disconnected from your real business model, customers, and goals. It’s a generic plan, suitable for anyone, and therefore, valuable to no one in particular.
Now ask to generate that same plan after connecting your own data: your company’s financials, customer insights, pricing, product descriptions, and marketing strategy. The AI now understands your unique strengths, competitive landscape, and brand tone. It can identify real opportunities, calculate feasible projections, and highlight specific risks relevant to your market.
How to Use Your Data
Since use of your own data is the key, a huge differentiator in choosing AI tools is access and use of your information.
Some, tools like ChatGPT, require you to manually connect your data sources, such as Gmail, Google Calendar, Outlook, Microsoft Teams, or SharePoint, before they can retrieve or process any content.
You can also upload files directly into project folders within ChatGPT or Claude to provide them with the context they need for a specific task.
Other tools, however, are natively embedded within your data ecosystems, meaning they effectively “sit on top” of your data and can interact with it automatically.
Gemini by Google is integrated into the Google Workspace environment, which includes Gmail, Google Docs, Sheets, Drive, Calendar, and Meet. Because it’s built directly into Google’s productivity tools, Gemini can easily access your data already stored within Google’s ecosystem.
Microsoft Copilot is embedded across Microsoft 365 applications, such as Outlook, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Teams, and SharePoint. It can leverage data from your emails, documents, chats, and calendars. In addition, it inherits existing security, compliance, and access controls.
Meta AI is integrated across Meta’s platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Messenger. It can access contextual and conversational data within these apps to help users draft posts, summarize messages, or retrieve shared content.
These integrated tools can access information and data in real-time without extra setup.
How Top AI Chatbots Handle Route Optimization
In this section, we illustrate with a real-life example why it’s important to test different AI tools for a specific business task.
The testing process described below took only a few hours to complete. The tools we used can be used at low cost of free of charge.
We selected four leading AI tools and evaluated them on a simple task of route optimization. The tools were chosen based on their popularity, connectivity and data-access capabilities:
- ChatGPT: a leading AI chatbot known for its versatility and ability to connect to various data sources.
- Gemini: deeply integrated with Google Workspace, providing seamless access to Gmail, Docs, Sheets, and other Google data.
- Microsoft Copilot: embedded within Microsoft 365, allowing direct interaction with Outlook, Teams, SharePoint, and related data.
- Claude: offers strong analytical capabilities and supports direct data uploads for custom analysis.
We tested these four AI chatbots on the same route optimization task to compare their performance and data-handling approaches.
Input
We created two files to support the test:
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) document in Microsoft Word, and
- Data file in Microsoft Excel.
The SOP stated:
“Our company operates three vehicles that deliver office supplies to various locations within the city of Edmonton, AB. The garage is located at 6510 Streetname Boulevard Northwest, Edmonton, AB T6H 5Z5. All three vehicles depart from the garage at the same time and return there after completing their deliveries.”
The Excel file contained the names and addresses of 25 schools across Edmonton, Alberta, representing our office supply delivery clients.
Prompts and Responses
We saved both the SOP and the data file on Google Drive, and then uploaded them to ChatGPT, Copilot, and Claude for testing.
The following prompts were used for each tool:
Gemini
“Access the Route Optimization folder on my Google Drive and optimize the delivery routes for December 3, 2025, clients. Distribute the delivery clients among three vehicles, arranging each route in sequential order to minimize overall travel time.”
Claude, ChatGPT, and Copilot
“Optimize the delivery routes for December 3, 2025, clients, using the attached list of clients and the SOP.
Distribute the delivery clients among three vehicles, arranging each route in sequential order to minimize overall travel time.”
Claude was unable to read the Excel file directly, so we had to copy and paste the table into the chat manually. Fortunately, the table contained only 25 rows.
As expected, the AI tools produced different route optimization results.
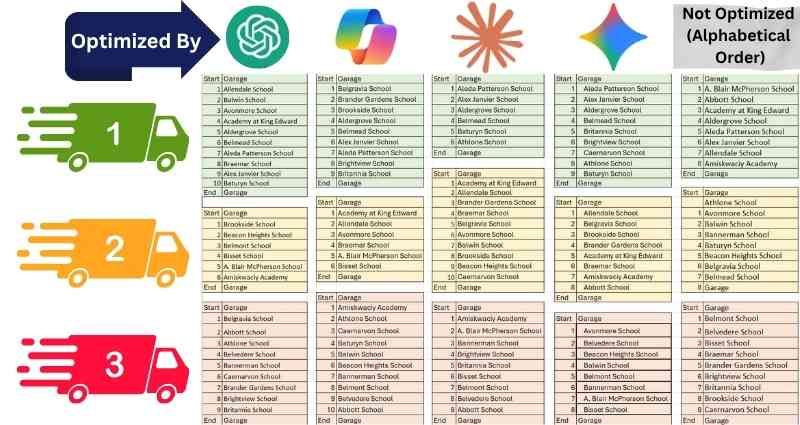
For comparison, we also created a baseline “non-optimized route”, which listed all 25 schools in alphabetical order and divided them into three approximately equal groups.
Validation of Results
To see how each tool handles real-world calculations, we asked all four to measure the total distance and travel time of the same non-optimized route for Vehicle #3.
Claude Approach
Claude was unable to perform live calculations, instead suggesting the use of external mapping tools:
“I don’t have the ability to directly calculate route distances and durations in real-time. However, I can help you get this information using available tools. Best options: Google Maps, Apple Maps, or route planning apps.”
Copilot Approach
Copilot provided a reasonable quite wide estimate range and offered practical suggestions for further optimization:
“? Estimated Trip Summary
- Total Distance: ~92–98 km (depending on traffic and exact routing)
- Total Driving Time: ~2 hr 15 min – 2 hr 30 min (without extended stops)
If you want to optimize the order (shortest time vs. shortest distance), tools like Google Maps or MapQuest Route Planner can reorder stops automatically.”
ChatGPT Approach
ChatGPT produced a model-based, but not map-based estimate using reasoned assumptions, also within a wide range:
“? Estimated Totals
| Metric | Estimate | Rationale |
| Total Distance | ≈ 82–90 km | Based on straight-line distance (~62 km) adjusted by a 1.35 urban driving factor |
| Total Driving Duration | ≈ 2 h 45 m – 3 h 15 m | Estimated using an average city driving speed of 27–33 km/h” |
Gemini Approach
Among the four tools, Google Gemini demonstrated the most accurate and data-driven estimation of travel duration and distance, due to its integration with Google Maps and access to real-time traffic data:
“The duration and distance for the trip visiting all the addresses, starting and ending at 6510 Gateway Boulevard NW, Edmonton, are:
• Duration: 2 hours and 57 minutes
• Distance: 144 km”
Gemini generated the most precise results accompanied by maps, reflecting its integration with Google Maps.
How We Validated the Results
We used Google Maps via Gemini as the benchmark tool for validation.
It was tasked with calculating the total driving distance and duration for all five route options, including both optimized and non-optimized versions.
The results are in the table below.
And the winner is…. ?

The clear winner of this exercise is Microsoft Copilot, which achieved the greatest reduction in both travel distance and duration, cutting the unoptimized route time by nearly half. Its results demonstrate the power of Copilot’s deep integration with Bing Maps, enabling it to perform effective route sequencing and generate practical, real-world optimizations.
A close second is Google Gemini, which also delivered strong optimization performance, significantly shortening total driving distance and time. Gemini’s strength lies in its native connection to Google Maps, allowing it to leverage accurate road data and real-time traffic conditions.
The other tools, like ChatGPT and Claude showed moderate or limited improvements, largely due to their lack of direct mapping integration.
Tools that are embedded within larger data and mapping ecosystems, like Copilot and Gemini hold a clear advantage in tasks that require geospatial analysis and real-world optimization.
Key Takeaways
- Your data is your competitive edge. AI tools trained on public data have broad general knowledge but lack insights specific to your business. Connecting your own data enables AI to generate outputs that are tailored and valuable to your organization.
- AI that uploads vs. AI that integrates. Some AI tools let you upload files directly to provide task-specific context, while others integrate natively within your data ecosystem. Examples of the later include Google Gemini for Google workspace users, Microsoft Copilot for Microsoft Office Users, and Meta AI for Facebook and Instagram users.
- AI variability can be managed. Results from AI models can range from highly accurate to completely off the mark. To manage AI variability, avoid random prompting. Instead, focus on a defined business task, experiment with tools, and refine your approach until you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Start with low-risk, repetitive processes.
- Different AI tools excel in different areas. Different AI systems excel in different areas. Claude produces more natural, human-like writing, while Microsoft Copilot leverages deep Bing Maps integration for spatial insights. Match each tool’s strengths to your specific use cases to maximize effectiveness.